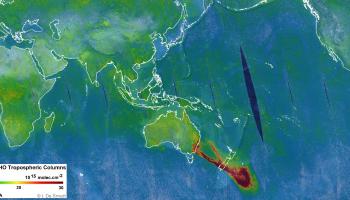
During the previous months, the exceptionally large wildfires in Australia were frequently mentioned in the news. As Royal Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, we are involved in space-borne and ground-based instruments that can detect such fires from space, in an indirect way. But what does this mean exactly, and how are these observations meaningful?
Even three years after the end of the Rosetta mission, comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko still hasn’t revealed all its secrets. Close to the end of the mission, a comet particle entered the ROSINA/DFMS instrument, which was designed to study only comet gas. In doing so, comet scientists discovered a group of less volatile substances known as "ammonium salts". This discovery explains why comets seem to contain so little nitrogen: the nitrogen is trapped in these substances that are difficult to detect from Earth. Ammonium salts are particularly intriguing because they contribute to the building blocks of life.
A long time ago (in 2008), in a place far, far above our heads, the SOLAR instrument, fixed on the outside of the International Space Station, started the mission it was designed for: to measure the radiation from the Sun from outside Earth’s atmosphere for a duration of 18 months, in order to compile a reference solar spectrum that is necessary for many fields of scientific research.
We are happy to announce we have received the ICOS label for the Maïdo station on Reunion Island. The station is now officially a part of the extensive ICOS (Integrated Carbon Observation System) network of measurement stations, which aims to provide long term observations of greenhouse gases for research, policy-making and the general public.
Michel Kruglansli, head of B.USOC (Belgian User Support and Operations Centre) at BIRA-IASB was interviewed by the french-speaking RTBF News about the Starliner test flight.
The Starliner was developed by Boeing, with the intention of replacing the Russian Soyuz rockets. The Soyuz are currently being used to bring astronauts to the International Space Station, and this costs the NASA and ESA quite a lot of money.
Although the unmanned Starliner capsule has not reached the ISS, it has safely landed back on Earth. A positive sign for the future!